How Solar Works
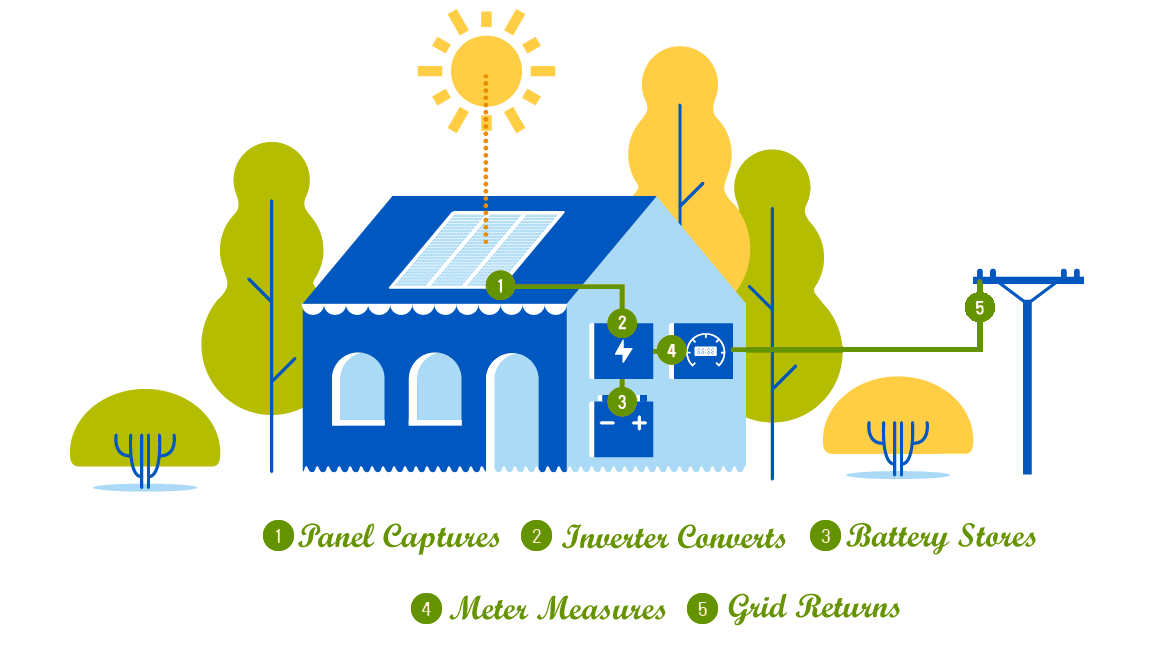
Adopting sunlight to control your house is quite simple. Initially, your solar boards will catch sunlight and adapt it specifically into energy. An inverter then changes over this energy into power you can use in your home. A battery will assist power your homes by saving away any abundance energy you deliver for later utilize. A few clients can likewise balance their bill if any additional energy is sustained again into the framework – that is the power of sun based solar energy.
ABOUT SOLAR
- Absorption of light that generates excitons or electron-hole pairs
- Separation of different types of charge carriers
- Separate extraction of carriers to external circuit
Photons in sunlight hit solar panel and they are absorbed by the semiconducting materials like Silicon
Electrons that are negatively charged are knocked loose from their atoms, which cause a difference in electric potential. Moreover, the current will start flowing through the material and cancels the potential. This electricity is captured and special composition of solar cells will cause the electrons to move in a single direction
The solar cells array will convert solar energy into usable direct current electricity
Selection of units to be used
Determination of wattage per unit
Determination of running hours of loads
Determination of total loads in watt-hours
To calculate energy in the system (Wh/day), multiply watts hours per day with 1.3 times
- 044 2242 1615
- starinverters@yahoo.com
- No.6,Kariyan Ponnan Street, Puzhuthivakkam, Madipakkam, Chennai-600 091
- No.6,Kariyan Ponnan Street, Puzhuthivakkam, Madipakkam,
Chennai-600 091 - 044 2242 1615
- starinverters@yahoo.com
Solar cell
Solar cell, which is also called as photovoltaic cell is an electrical device. Using photovoltaic effect this device converts light energy into electricity. Solar cell is also a form of photoelectrical cell that can generate and support electric current when exposed to light without the need to be attached to an external voltage source. The electrical characteristics of photoelectrical cell may vary such as voltage, current or resistance when exposed to light.
The word “Photovoltaic” refers to “light” from “volt” and it is in use in English since 1849. Photovoltaic is derived from the Greek work, ῶς (phōs), which means light and Volt is derived from the last name of an Italian physicist, Alessandro Volta, who is the inventor of a battery. Volt refers to the unit of electro-motive force.
Photovoltaic is a part of technology and research, which relates to the practical application of photovoltaic cells, particularly in producing electricity from light. It is very often used to generate electricity from sunlight. However, these cells can also be described as photovoltaic even when light sources like artificial light, lamplight, and others used apart from sunlight. At this instance, cell is used as photo detector, such as infrared detectors to detect light or electromagnetic radiation near visible range.
Three basic attributes used for the Photovoltaic cell operation
The solar thermal collector will collect heat by absorbing sunlight for direct heating or indirect generation of electrical power. The photoelectrolytic cell refers to a type of photovoltaic cell, which is developed by modern dye-sensitized solar cells or it may also refer to a device that splits water into oxygen and hydrogen with the help of solar illumination.
Solar Panel Building Block
The photovoltaic cells assemblies are used majorly to make solar modules. This helps to generate electrical power from sunlight. Multiple cells, which are in an integrated group and oriented in one plane will constitute solar photovoltaic panel or solar photovoltaic modules that are as distinguished from the solar hot water panel or solar thermal module.
Solar power is the electrical energy generated from solar modules. Solar energy is an example of solar power. Group of solar modules connected to each other is called “array”.
Daryl Chapin, Gerald Pearson, and Calvin Souther Fuller developed the first practical photovoltaic cell at Bell Laboratories in 1954.
Photovoltaic Cells
The solar cells are electrically connected and encapsulated as module. These photovoltaic modules have glass sheet on the front, which is the sun up side and allows light to pass. It also protects semiconductor wafers from the abrasion and impact caused due to wind-driven debris, hail, rain and other damaging sources. The solar cells are connected in series of modules, which create additive voltage. Parallel connected cells can yield higher current; however, parallel connections may cause some significant problems such as shadow effects that may shut down weaker parallel string that is less illuminated. This may cause substantial power loss while damaging weaker string due to excessive reverse bias applied to the shadowed cells by the illuminated partners.
The series cells strings are handled independently and they are not connected in parallel. It is, however, possible to interconnect modules to create an array using desired peak DC voltage with loading current capacity and independent MPPTs to achieve a better solution.
In case of absent of paralleling circuits, it is possible to use shunt diodes to especially reduce power loss due to shadowing in arrays with parallel or series connected cells. However, for the practical use of solar-generated energy, electricity is fed into electricity grid using inverters in a stand-alone system. The batteries are used for storing energy and solar panels are used to recharge or power portable devices.
Working of Solar Cells
Polycrystalline Silicon or Multicystalline Silicon
The polycrystalline silicon or multicrystalline silicon is made from cast square ingots, which are the large blocks of molten silicon that are carefully cooled and solidified. It is less expensive to produce Poly-Si cells than single crystal silicon cells, however, it is less efficient. According to a data produced by the United States Department of Energy, the sales of polycrystalline are higher than monocrystalline silicon.
Lifespan
The solar panels are commercially available for twenty years since and they are widely used for producing electricity. The manufacturers of solar panels give 90% of warranty of rated output for first 10 years and 80% for second 10 years. However, these panels are expected to function well for up to 35 years.
Solar Radiation data in India
The location of India has made the country to be the rich source of solar energy. Located in the earth’s equatorial Sun Belt, India receives about 5000 trillion kWh solar power per year. Moreover, 300 clear sunny days per years adds to the advantage of solar power source in India. Based on the location, the daily solar energy incident on an average over India would vary from 4 to 7kWh/m2 with 2300 to 3200 sunshine hours per year. This is absolutely higher than the total consumption of current energy. The global radiation in the north-eastern region and hilly areas on an average per day is 5kWh/m2 and it is 7kWh/m2 in the western regions and cold desert regions.
The global radiation would vary annually from 1600 to 2200KW/m2. The annual global radiation in the regions like Rajasthan, Tamil Nadu, Northern Gujarat and few parts of Ladakh, Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, Maharashtra and Madhya Pradesh is large compared to other parts of the world like Europe, Japan, and US, where the development and deployment of solar technologies are higher. This indicates that solar power projects can be commercially implemented in various regions of India.
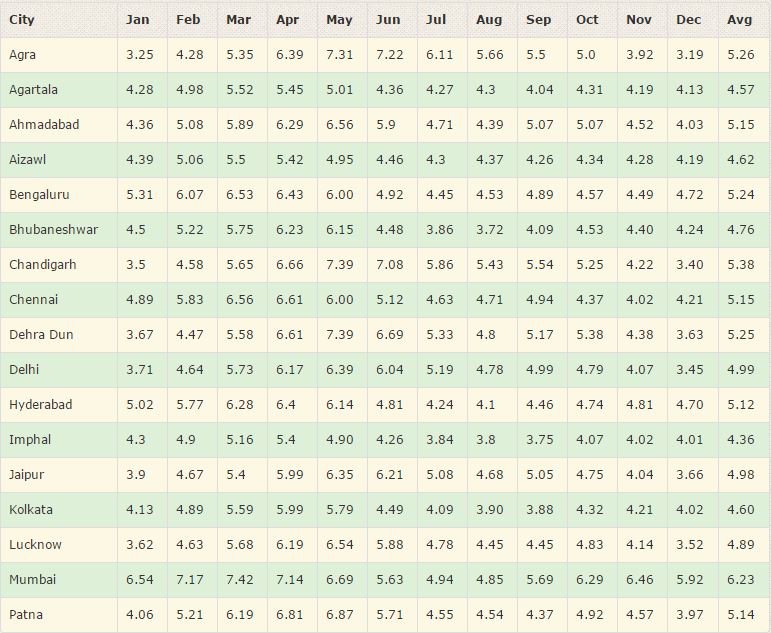
Tamil Nadu receives the third largest amount solar radiation next to Rajasthan and Gujarat. Tamil Nadu receives 5.35KWh/sq.m/day. Many companies are not taking initiatives to implement the solar power projects in their premises in Tamil Nadu.
Solar radiation Data in India
General
Photovoltaics is used to convert light into electricity directly. Materials like silicon releases electrons naturally when exposed to light, however, these electrons can be harnessed for producing electric current. Many thin silicon wafers are wired together and enclosed in a rugged protective panel or casing. To run a standard household electric appliance, the PV panels that can produce direct current electricity is converted to an alternative current electricity. An inverter connected to PV panels is used for converting direct current electricity into alternative current electricity. Watts (W) is used to measure amount of electricity produced, whereas, kilowatt (KW) equals 1,000 watts and Megawatt (MW) equals 1,000,000 watts or 1,000KW. Kilowatt-hours (KWh) are used to measure amount of electricity used over a specific time period.
Solar rating refers to the measure of an average solar energy, which is also called as Solar Irradiance available at a specific location on an average in a year. Radiant power is expressed as Watts/sq-meter or KW/sq meter, which is power per unit area. Total daily irradiation, which is Wh/sq-meter, is calculated using irradiance values W/sq-meter.
Shading
There is a possibility for the solar energy system to dramatically reduce its output when the solar collectors or solar panels get any shading during the daytime. This is the fact with photovoltaic solar panels, as any partially shaded PV panel can result in power loss across PV array.
Some of the solar incentive programs include;
(Example of Solar Electric (PV) System Calculations)
Estimation of the size of Solar Electric (PV) system: Solar Panels
The modern PV solar panels on an average can produce 8 – 10 watts per square foot of solar panel area. Ex: 20ft x 10 ft = 200 sq.ft area, which can product 9 watts per sq.ft and thus the overall production would be 200sq.ft x 9watts/sq.ft = 1,800 watts of electric power.
Converting Watts or KW to Energy (KWh)
1 KWh refers to 1000watts of energy for one hour. A solar energy system can generally provide output for 5 hours per day, therefore a 1.8 KW system size producing electricity on an average 5 hours a day, and 365 days a year can annually produce, 3,285 KWh.
At the same time, if the PV panels are shared for a part of the day, then the output can be reduced according to the percentage shared. For instance; if the PV panels receive direct sun light for 4 hours a day versus standard 5 hours, and panels are shaded 1 divided by 5 = 20% of time, whereas 80% of time is assumed direct sun light hours received. Therefore, the output per 200 sq.ft PV panel system will be 3,285 KWh per year x 80% = 2,628 KWh per year.
Estimation of the size of Solar Electric (PV) system to replace Specified amount of Utility (grid) electricity
Roughly calculate PV System Capacity required (KW of PV):
Annual electricity usage = Monthly Usage x 12 months
Electricity usage is experessed in KWh
KW of PV = (Annual Usage) / (78% x KWh/KW-year from Solar Radiance)
Chart as follow
Panel: Cells arranged in series or parallel connection
Array: Number of solar panels connected together in a single structure
Array Load: Maximum load connected to the panel
Array size: Size of the panel to be connected to meet required load amount
Solar Insolation: Amount of sunlight received on a given surface area in a given time, KWh/m2/day
Inverter: Electrical device used for converting direct current from panel to alternative current to the transformer
Charge controller: Used for controlling battery to prevent overcharging of discharging
Battery: Battery is determined by the amount of electrical energy it can deliver over a specified time period, which is measured in Ampere hours (Ah) when discharged at a uniform rate over a specified time period.
Load Requirement
About Us
Star Solar Power is formed by a team of environmentally attentive MSME Trained entrepreneurs who wish to ensure a sustainable future in Solar systems. The core management team is formed of people with rich experience in small-scale and large-scale trading in India.
REACH US
From The Gallery
+ View MoreReach Us
Star Solars
Latest Blog Post
Maecenas laoreet lectus est, eget ultricies eros. Aliquam ipsum nunc, tincidunt non fringilla.Maecenas laoreet lectus est, eget ultricies eros. Aliquam ipsum nunc, tincidunt non fringilla.
+ Read More












